Correctly Label The Following Structures of The Female Reproductive System
Welcome to my article on correctly labeling the structures of the female reproductive system! As a seasoned expert in the field, I am excited to share my knowledge and insights with you. Understanding the intricacies of the female reproductive system is not only fascinating, but also essential for anyone interested in women’s health and wellness.
The Importance of Correctly Labeling Structures of The Female Reproductive System
Enhancing Medical Education And Communication
Accurate labeling of the structures of the female reproductive system plays a vital role in enhancing medical education and fostering effective communication among healthcare professionals. By correctly identifying and labeling these structures, medical students and professionals can develop a comprehensive understanding of the female reproductive system, its functions, and potential abnormalities.
When healthcare professionals have a clear understanding of the structures, they can effectively communicate with their colleagues, patients, and other members of the healthcare team. Clear and precise labeling enables seamless information exchange, reducing the risk of miscommunication and ensuring that everyone is on the same page when discussing diagnoses, treatment plans, and surgical procedures.
Ensuring Accurate Diagnosis And Treatment
Properly labeling the structures of the female reproductive system is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. With precise labeling, healthcare professionals can identify any abnormalities or potential issues within the reproductive system and formulate appropriate treatment plans.
In gynecology and obstetrics, accuracy is paramount. Any mislabeling or misinterpretation of structures can have serious consequences for patients. For example, misidentifying a fallopian tube or an ovary can lead to incorrect treatment decisions, delayed diagnosis, or even unnecessary surgeries.
By ensuring accurate labeling, healthcare providers can provide better patient care, leading to improved health outcomes for women. Clear communication through accurate labeling supports the delivery of personalized, evidence-based care that addresses the specific needs of each patient.
Correctly labeling the structures of the female reproductive system is crucial for enhancing medical education, facilitating effective communication between healthcare professionals, and ensuring accurate diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing the significance of accurate labeling, healthcare providers can work together to deliver optimal care and improve women’s overall health and well-being.
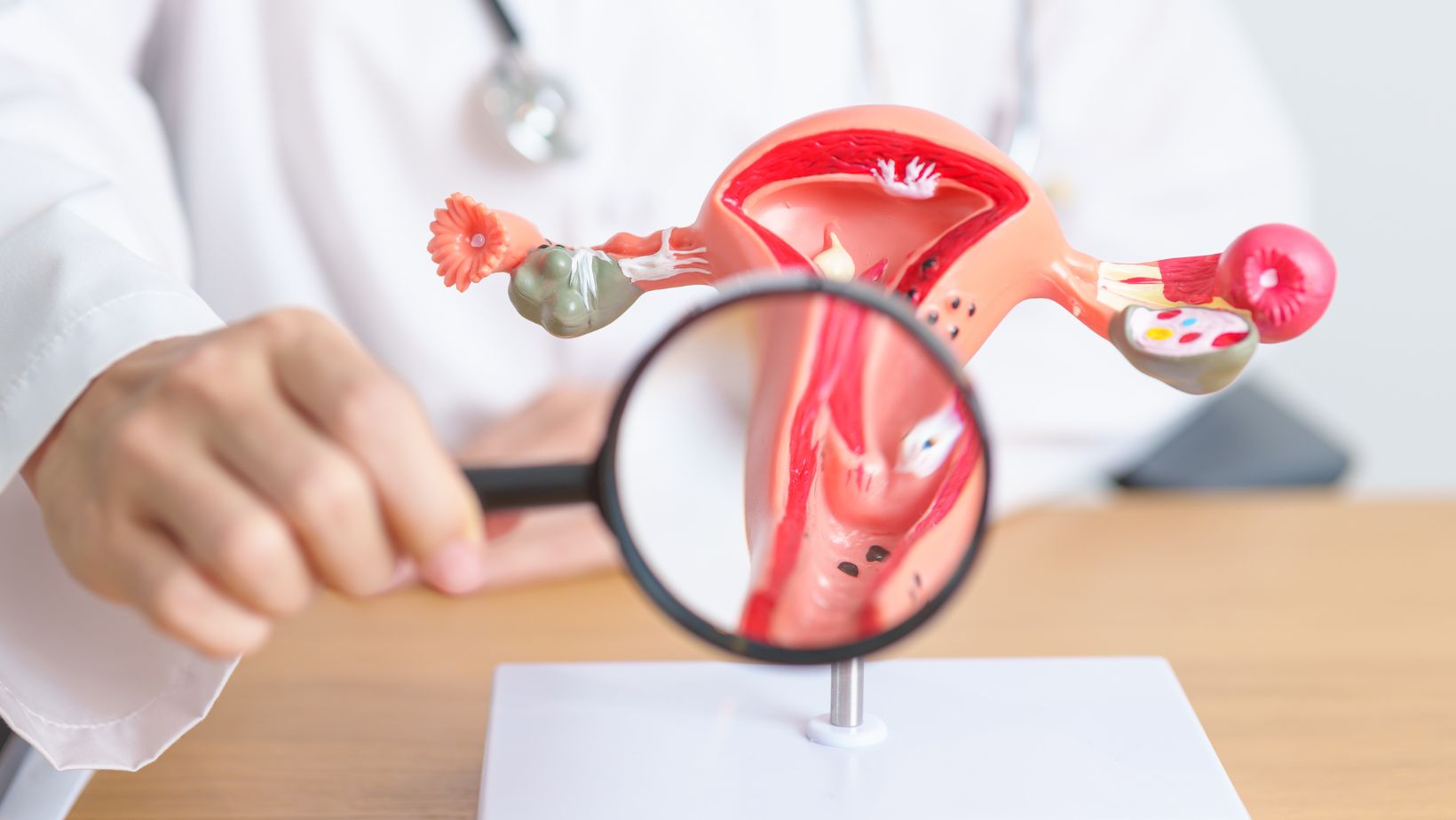
Understanding The Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is a complex and intricate system that plays a crucial role in reproduction and overall health. It is essential to correctly label the structures of this system to ensure accurate communication and understanding among healthcare professionals. In this section, I will delve into the external and internal structures of the female reproductive system.
The External Structures
The external structures of the female reproductive system include the vulva, clitoris, and the labia majora and minora. These structures are responsible for protecting and supporting the internal reproductive organs. Here’s a closer look at each of them:
- Vulva: The vulva encompasses the external genitalia of a woman. It consists of the mons pubis, which is a fatty tissue above the pubic bone, the labia majora, and the labia minora. The vulva acts as a protective barrier for the internal structures.
- Clitoris: The clitoris is a highly sensitive organ located at the front junction of the labia minora. It plays a crucial role in sexual pleasure and arousal.
- Labia majora and minora: The labia majora are the outer folds of skin surrounding the vaginal opening. They serve to protect the internal reproductive structures. The labia minora are the inner folds of skin that protect the vaginal opening.
The Internal Structures
The internal structures of the female reproductive system include the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Each structure has a unique function and plays a vital role in reproduction. Let’s explore them further:
- Vagina: The vagina is a muscular canal that connects the external structures to the uterus. It serves as the birth canal during childbirth and also allows for the passage of menstrual blood.
- Cervix: The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. It plays a crucial role in pregnancy, allowing sperm to enter the uterus and menstrual blood to flow out.
- Uterus: The uterus, also known as the womb, is a pear-shaped organ where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus. It undergoes monthly changes to prepare for pregnancy and shed the lining during menstruation.
- Fallopian Tubes: The fallopian tubes are thin, tube-like structures that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They serve as the pathway for the egg to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. Fertilization of the egg by sperm typically occurs in the fallopian tubes.
- Ovaries: The ovaries are two small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. They produce and release eggs during ovulation and also produce hormones, including estrogen and progesterone.
Conclusion
Accurately labeling the structures of the female reproductive system is crucial for medical education and effective communication among healthcare professionals. By utilizing anatomical diagrams and models, studying comparative anatomy, and engaging in hands-on practice, healthcare professionals can enhance their understanding of these structures and improve their accuracy in identifying and discussing them. This knowledge not only benefits individual healthcare professionals but also contributes to improved communication and collaboration among colleagues.
Correctly labeling the structures of the female reproductive system is a fundamental aspect of medical education and healthcare practice. By employing the techniques discussed in this article, healthcare professionals can enhance their knowledge, improve communication among colleagues, and ultimately provide optimal care for women’s reproductive health.